Lesson 6: ISPMs and the NPPO
Topic 4: Import and Export Operations
Pest detection is relevant to both the import and export operations of an NPPO.
Objectives:
- Pest Detection
- Describe good surveillance practice (ISPM 6)
- Distinguish between general surveillance and specific surveys (ISPM 6)
- Describe objectives and assumptions of inspection and the procedures involved in inspection (ISPM 23)
- Describe objectives of sampling consignments (ISPM 31 and associated explanatory document)
- Distinguish between statistically-based and non-statistical sampling (ISPM 31 and associated explanatory document)
Pest Detection: Surveillance, Inspection, and Sampling (ISPMs 6, 23, 31)
Surveillance, inspection, and sampling are critical to an NPPO’s import and export pest-detection functions.
Importing countries use surveillance to determine which pests are present in their territories. They also use surveillance to determine potential quarantine pests and to begin eradication or control programs. Exporting countries use surveillance to demonstrate pest absence or to demonstrate that consignments originate in a “pest-free area”.
Inspection is the most frequently used procedure to determine if pests are present in consignments of regulated articles in international trade. Inspection is an essential tool for importing countries in managing pest risks associated with importing commodities. Exporting countries use inspection to determine if consignments are in keeping with importing country requirements.
Sampling is the basis for inspection protocols for import and export pest detection. Sampling is also the basis for surveys to determine if a pest is present in a geographic area.
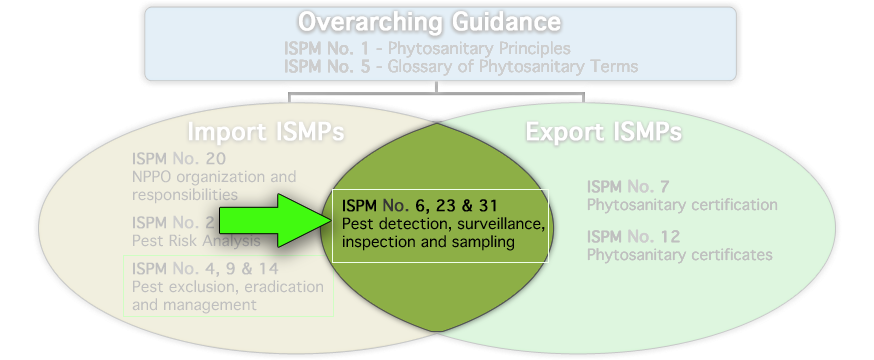
ISPM 6: Guidelines for Surveillance
Category:
Import and Export Systems and Operations
Purpose of the standard:
ISPM 6 describes survey and monitoring systems that provide information for NPPOs to use in establishing pest-free areas, in preparing pest lists, and in pest risk analysis (PRA).
Summary of standard:
There are two types of surveillance systems: general surveillance and specific surveys. General surveillance relies on available information, for example, from domestic or international agencies, universities, producers, consultants, and trade journals. This information can be used to support declarations of pest freedom, host and commodity pest lists, and distribution records. Specific surveys are official detection, delimiting, or monitoring surveys that identify a target pest and a specific geographic area, production system, or season. Specific surveys describe the statistical basis and survey methodology.
Good surveillance practice requires that personnel involved in general surveillance should be trained in plant protection and data management. Personnel involved in specific surveys should be trained in sampling methods, sample preservation, and transport of samples for identification and record keeping. Appropriate equipment and supplies should be used, and methodology should be technically valid.
ISPM 23: Guidelines for Inspection
Category:
Import and Export Systems and Operations
Purpose of the standard:
The purpose of this standard is to describe procedures for the inspection of consignments at import and export. The objective of inspection is to confirm compliance with requirements relating to quarantine pests for both imported or exported consignments. Inspection may also be used generally to detect pests.
Summary of the standard:
A PRA is used to develop lists of regulated pests for which inspection is appropriate and/or to identify commodities that should be inspected.
During visual examination, a sample is taken from the consignments to determine if the pest is present. Inspection can be used to detect pests and to verify compliance with other requirements, such as treatment, freedom from contaminants, required growth stage, origin of consignment, and point of entry.
Inspection involves three separate procedures: examining documents associated with a consignment, verifying consignment identity and integrity, and visual examination for pests and other phytosanitary requirements.
The suppositions on which inspection is based are that: pests or their symptoms are visually detectable, inspection is operationally feasible, and recognition that pests might not be detected by inspection.
ISPM 31: Methodologies for Sampling of Consignments
Category:
Import and Export Systems and Operations
Purpose of the standard:
The purpose of the standard Methodologies for Sampling of Consignments is to provide guidance to NPPOs in selecting appropriate methods to sample consignments for inspection or testing.
Summary of the standard:
Statistically-based sampling can provide a level of confidence that the incidence of a pest is below a certain level, but cannot prove that a pest is absent from a consignment.
Some of the objectives of sampling consignments are to:
- Detect regulated pests
- Verify compliance with phytosanitary measures
- Determine that the number of pests do not exceed specified tolerance levels
- Provide assurance of the general phytosanitary condition of a consignment
- Detect organisms for which a risk has not yet been determined
- Determine the proportion of the consignment that is infested
Sampling for phytosanitary inspection is done by taking units from the consignment without replacing the units selected. NPPOs may use a statistically-based or non-statistical sampling methodology. Selection of an appropriate sampling method should be in keeping with NPPO objectives, should be well documented, and should be operationally feasible.
Statistically-based sampling is designed to detect a certain percentage or proportion of infestation with a specific confidence level and requires the NPPO to determine the acceptance number, the level of detection, confidence level, effectiveness of detection, and sample size. Examples of statistically-based sampling methods include random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, sequential sampling, cluster sampling, and fixed-proportion sampling.
Non-statistically based sampling is used when the goal is only detection of pests, and it includes methods such as convenience sampling (most accessible, cheapest, fastest), haphazard sampling (selecting arbitrary units without randomization process), and selective or targeted sampling (choosing parts of the lot most likely to be infested).
Surveillance, inspection, and sampling are ways both import and export NPPOs can monitor and detect pest levels.
To continue, select Lesson Summary from the Topics menu above or click here.